Japan PM Meets Bill Gates; Pledges $550 Million for Global Vaccine Initiative
- Japan pledges $550 million for vaccines in developing countries over five years.
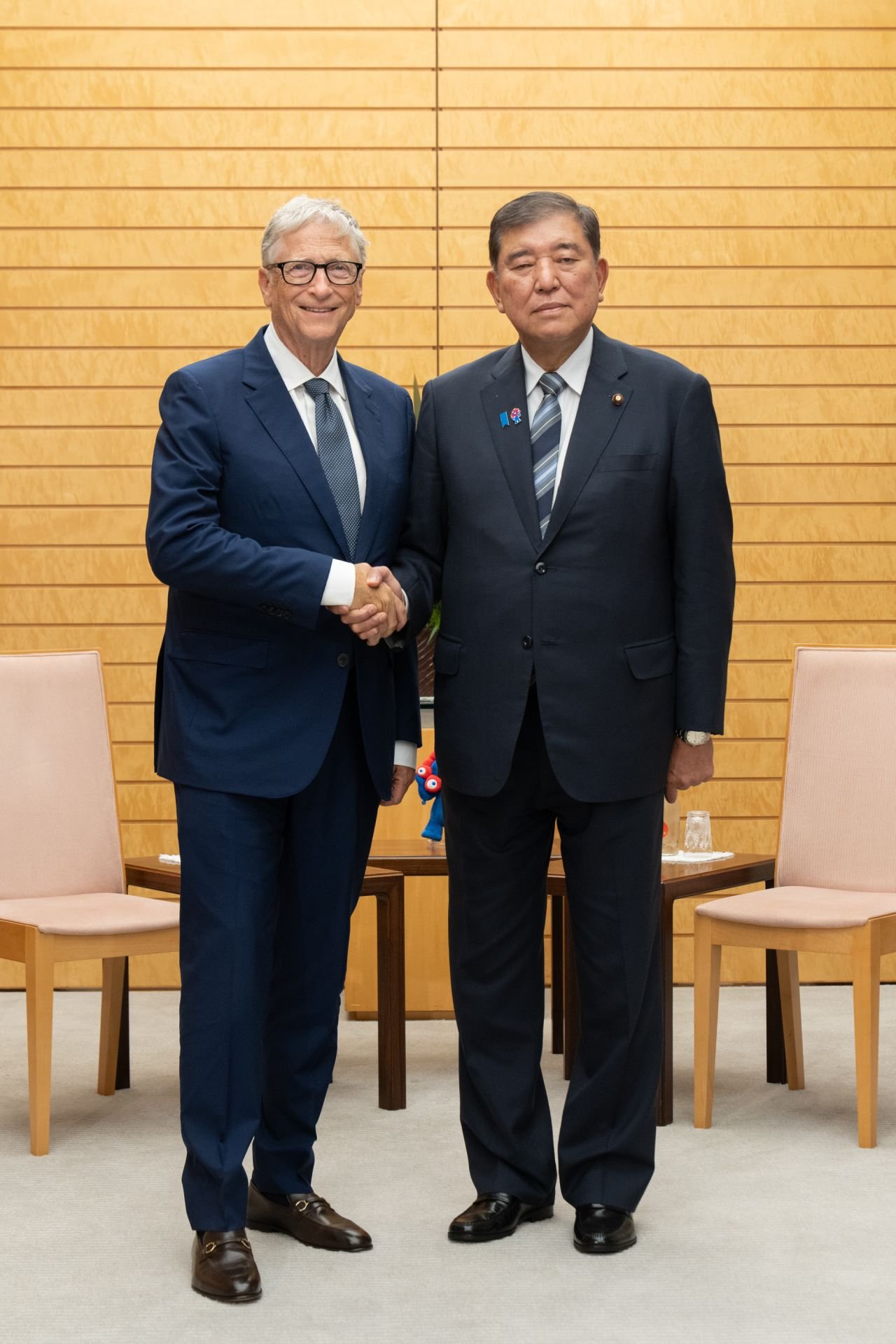
- Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba announced this with Bill Gates in Tokyo.
- The pledge aligns with Gates’ vision for global health improvement.
- Japan aims to strengthen ties with Africa through this initiative.
- The commitment will be highlighted at the upcoming TICAD conference.
Japan has announced a significant financial commitment to global health, pledging up to $550 million over the next five years to support an organization dedicated to providing vaccines to children in developing countries. This announcement was made by Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba during a meeting with Microsoft Corp. founder Bill Gates at the Prime Minister’s office in Tokyo. Gates, a well-known advocate for global health, supports the international organization that will benefit from Japan’s contribution.
Tetsuo Saito, head of the Komeito party and a participant in the meeting, conveyed Ishiba’s respect for Gates’ efforts in global health. Ishiba expressed Japan’s intention to make a substantial contribution to this cause, aligning with Gates’ vision for improving health outcomes worldwide. This financial commitment is expected to be officially announced at the Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD), scheduled to take place in Yokohama.
The conference, spanning three days, will serve as a platform for Japan to strengthen its ties with resource-rich emerging nations. By investing in the health of children in developing countries, Japan aims to foster goodwill and collaboration with these nations, which are crucial partners in global development. This initiative is part of Japan’s broader strategy to enhance its diplomatic and economic relationships with African countries.
Strengthening Ties with Africa
The Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) is also working to establish connections between Japanese cities and African nations. This initiative involves designating certain Japanese cities as “hometowns” for African countries, facilitating two-way exchanges of human resources. Such efforts are expected to contribute to Japan’s national interest by fostering personnel who can serve as links to Africa, a continent poised to play a pivotal role in global development due to its growing population.
The TICAD conference has a rich history of promoting development in Africa. Since its inception in 1993, the conference has evolved into a key platform for dialogue and cooperation between Japan and African nations. Over the years, TICAD has facilitated numerous initiatives aimed at addressing critical issues such as infrastructure development, regional conflict prevention, and health promotion. The Yokohama Declaration, adopted during a previous TICAD conference, emphasized the importance of these areas and reaffirmed the necessity of supporting child health and maternal mortality reduction efforts in Africa.
Japan’s commitment to global health is not new. The country has a long-standing tradition of contributing to international development efforts, particularly in the field of health. This latest pledge is a continuation of Japan’s efforts to support global health initiatives and improve the well-being of children in developing countries. By investing in vaccines, Japan is addressing a critical need in these regions, where access to essential healthcare services is often limited.
Collaborative Efforts for Global Health
The partnership between Japan and Bill Gates is a testament to the power of collaboration in addressing global challenges. Gates, through his philanthropic efforts, has been a driving force in the fight against infectious diseases and has played a significant role in advancing global health initiatives. His collaboration with Japan underscores the importance of partnerships between governments and private sector leaders in tackling complex global issues.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges posed by infectious diseases, Japan’s commitment to vaccine distribution in developing countries is a timely and necessary intervention. Vaccines are a critical tool in preventing the spread of diseases and improving health outcomes, particularly in regions where healthcare infrastructure is lacking. By investing in vaccines, Japan is not only contributing to the health of children in developing countries but also strengthening its diplomatic ties with these nations.
The upcoming TICAD conference will provide an opportunity for Japan to showcase its commitment to global health and development. The conference will bring together leaders from Japan and African nations to discuss strategies for addressing pressing issues such as health, infrastructure, and economic development. Japan’s pledge to support vaccine distribution is expected to be a key topic of discussion, highlighting the country’s dedication to improving health outcomes in developing regions.












Post Comment